Circular Economy

Materials
Pump element:
Plastic, ABS (durable, waterproof, bad for environment)
Pump
Electronic “brain”
Cables
Power Supply + cable
Magnets (connectors for electricity between units)
Water tube, Silicone
Pot element:
Plastic, ABS:Top element and bottom element
Valve
Led Strip
Magnets
Cable
Water tube, Silicone
Pot cup:
ABS
Heat sealed top lid that can be peeled off
Soil
Plant
End of Life
The topic End of Life concerns the awareness of where your product will be after its lifetime. In the ideal situation every possible element required to produce a new product would be gained from already existing materials originating from previous products and materials. This means a reduction in obtaining raw materials. When this is implemented throughout the whole economy,
The base of striving towards a circular economy is tracking how components and materials move. Nowadays, we mostly make use of a linear economy. Linear means materials will be disposed of after the lifetime of the product. This means we take, make, use, and dispose.
To develop into a cycle, ‘closing the loop’ is the key phrase. This implies the use of materials and components that already exist, so not always using virgin/raw materials. Solely when there this is called a circular economy. is no other alternative. There are different methods to close the loop. From high to low value preservation: reuse, repair, refurbish, remanufacture, retrieval and recycle.

Materials
It has been chosen to use ABS, which is waterproof and inexpensive. All parts (except the electronics, water tube, and LED strip) are made out of ABS. To facilitate efficient maintenance, the wires and electronics have good accessibility.
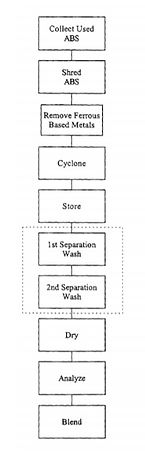
This makes recycling the product relatively easy for the company and its customers. By making recycling simple, you increase the amount of material that can be reused again to close the loop. To recycle ABS, the following process is used (see below). If the costs allow it, recycling at the location of the production is preferred, as this will reduce the transportation costs and emissions. First, the used ABS is collected from products which were broken and not suitable for repairs. The material is then shredded to granulates. Subsequently, the ferrous based materials, such as iron, can be collected via a magnet. For another method of separation, a cyclone is used. This is a machine which separates the materials based on their density. It works with centrifugal forces. After this, the ABS is stored until it is treated further.
To continue with the process, a dual separation wash is applied to remove any remaining unwanted metal or plastic granulates. In this ‘wash’ the heavier materials sink to the bottom. After the wash the material needs to dry.
The recycling is completed at this point. The material needs to be analysed if it has the desired characteristics. Other characteristics can be reached when it is blended with other materials.
However, to keep as much value as possible, the different methods to close the loop should all be considered. The smaller the loop, the more value you preserve. This means that Clover5 wants to reuse and repair, rather than re-manufacture and recycle. An emphasis is placed on the maintenance of the product. There will be investment in maintenance experts, which will be able to repair the products with minor flaws. This is inspired by the facility of StrucMac.
Image Source: ABS recycling process - European Patent Office - EP 1036641 A1
Repairs
The latter mentioned that we see StrucMac as a form of inspiration. It is a facility where they rent out machines as band saws or boring mills. To quote from their website: “StrucMAC offers a full service solution that runs through the manufacture, assembly and installation cycle. We have the skills and equipment to fabricate any size and type of steel requirement”.
Part of our company has such a service as well. The pots and pumps are rented out to the customer. Therefore, we would like to invest in a sort of workplace, which is devoted to the repairment of the pots and pumps. Preferably this would be close to the customer, to deliver a service which is fast and efficient. Furthermore, it can reduce transportation costs and emissions. However, it would be more costly to hire technicians in a richer country. This is a compromise that must be considered.
To conclude, Clover 5 will focus on the repairment in the cycle. There is extra money invested in the expertise of the renovation of the products. All parts of ABS which cannot be used anymore, or are broken down, are recycled. These two actions will reduce the amount of waste and strive towards a circular economy. This will benefit the company in the long term, as less resources are needed as well. Plus, it is more likely that companies will want to invest in our project, as it will benefit the image of the company.